Outcomes of primary simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplants by induction agent in the United States
Adam Cerise3, Scott Jackson2, Raja Kandaswamy3, Samy Riad1.
1Nephrology , University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, United States; 2Complex Care Analytics , MHealth Fairview , Minneapolis, MN, United States; 3Surgery , University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, United States
Background: Induction immunosuppression choice for simultaneous pancreas-kidney (SPK) transplants varies widely in the United States. We examined the association between induction agents and outcomes of SPK recipients discharged on tacrolimus and mycophenolate.
Methods: We used the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients to examine all primary SPK transplants between 2000 and 2020, excluding crossmatch positive recipients and those with other induction regimens. We grouped recipients according to induction regimen used into three groups: anti-thymocyte globulin (n=5678), alemtuzumab (n=1199) and IL-2 RA (1593). Delayed graft function, acute kidney and pancreas rejection rates were compared by type of induction. We analyzed the ten-year recipient and composite (kidney and pancreas) grafts survival using Kaplan-Meier survival function. Cox proportion hazard models were utilized to examine the association between induction type and the ten-year recipient and grafts survival. Models were adjusted for recipient age, sex, ethnicity, HLA-MM, diabetes type, dialysis dependency, cold ischemia time, local vs imported organs, PRA, steroid maintenance and PDRI.
Results: Delayed graft function rate was observed in less than 6.5% of the recipients and did not differ between groups P=0.68. One-year kidney rejection rates were observed in 8.9% of the anti-thymocyte group, 9.5% of the IL-2RA group and 13% in the alemtuzumab group (p<0.001). Similarly, one-year pancreas rejection rates were observed in 9.5% of the anti-thymocyte group, 12.4% of the IL-2RA group and 14.1% in the alemtuzumab group (p<0.001). In the univariable analysis, induction type was not associated with recipient (log-rank p=0.11) or grafts survival (log-rank p=0.36). In the multivariable model for the composite grafts survival, alemtuzumab use was associated with 22% increased kidney or pancreas graft loss compared to anti-thymocyte globulin (LLCI, aHR, ULCI) (1.05, 1.22, 1.42), while IL-2RA use was not a predictor of worse grafts survival. Induction type didn’t influence recipient survival in the adjusted model.
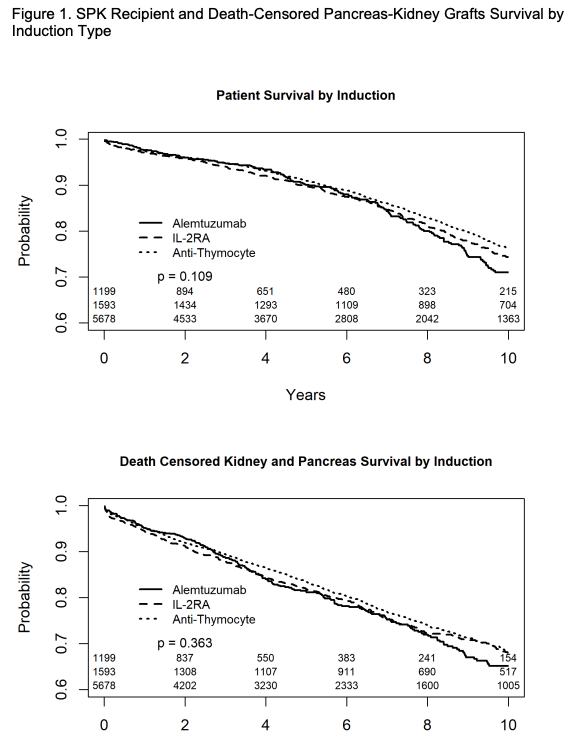
Conclusion: r-ATG use was associated with the lowest kidney and pancreas rejection rates. Compared to r-ATG, alemtuzumab but not IL-2RA was associated with worse long-term death-censored SPK grafts outcome. Our analysis supports the US national popularity of r-ATG induction in primary SPK recipients.

right-click to download
