Outcomes in mild obese recipients with diabetes mellitus type 2 that received simultaneous kidney pancreas transplant
Massini Merzkani 1, Haris Murad1, Mei Wang1, Wenjun Hu1, Mengmeng Ji1, Omar Alhomar1, Obadah Alzahabi1, Yazen Al-Hosni1, Mohamad Zayed1, Jason Wellen1, Krista L Lentine 2, Su-Hsin Chang1, Tarek Alhamad1.
1Washington University School of Medicine at St.Louis, Saint Louis, MO, United States; 2Saint Louis University School of Medicine, Saint Louis, MO, United States
Objective: Simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplant (SPKT) has excellent outcomes in patients with end stage renal disease secondary to diabetes mellitus type 2 (DMT2). The outcome of SPKT in DMT2 obese recipients with Body Mass Index (BMI) >30 kg/m2 has not been well studied.
Methods: We reviewed Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) data that had SPKT for DMT2 between 1/1/2000 and 6/12/2020. Patients with age <18 years, BMI<20 kg/m2 and ≥35 kg/m2, prior transplants and donors after cardiac death were excluded. Obesity was defined as having a BMI between the ranges 30.0-35.0 kg/m2 and lean recipients with BMI 20.0-29.9 kg/m2. The outcomes were kidney and pancreas graft loss and death at post-SPKT 1, 5, 10 years, and the entire follow-up. The association of obesity with each outcome was analyzed using multivariable Cox regression including adjustment for recipient, donor, and transplant characteristics.
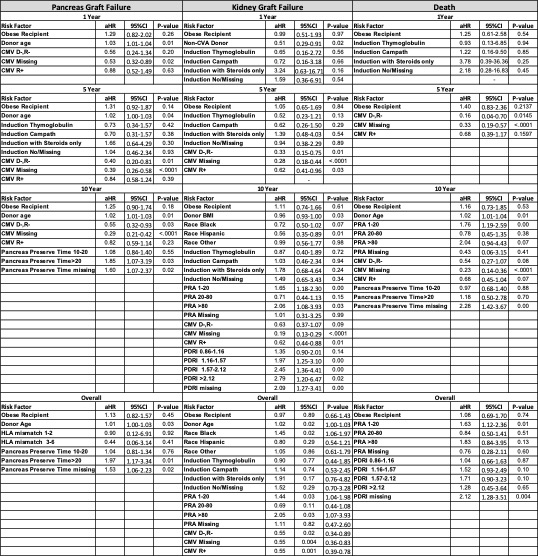
Results: A total of 1,311 SPKT with DMT2 were analyzed. Obesity in SPKT with DMT2 did not increase the risk of kidney or pancreas allograft failure (aHR=0.97,95% CI [0.66-1.43]; aHR=1.13,95%CI [0.82-1.57]). Similar results were observed at 1, 5 and 10 years. Similarly, obesity was not associated with an increased risk for death aHR=0.97, 95%CI[0.66-1.43] at all follow-up time points.
Conclusion: SPKT recipients with obesity and DMT2 were not at increased risk of death and kidney or pancreas allograft failure. This study encourages many centers to not exclude patients with DMT2 with obesity for SPKT, which can benefit survival and decrease DM complications.

right-click to download
