Seroconversion after vaccination with BNT162b2 Pfizer/BioNTech, ChAdOx1 nCoV-19/AZD1222 and coronavac against sars-cov-2 among hemodialysis and kidney transplant patients
Alfredo Chew-Wong1, Lizbeth Morales-López1, Elizabeth Hernández-Infante1, José M. Arreola Guerra1, Guadalupe Ricalde-Ríos1, Isis A. Velázquez-Ramírez1, Luis Romo-Franco, 1, Ana B Lagunas-Rodriguez1, Mario González-Gámez1, Rafael Reyes-Acevedo1.
1Nephrology and Kidney Transplantation, Centenario Hospital Miguel Hidalgo, Aguascalientes, , Mexico
Background: Since December 2019 the world has been affected by the SARS-CoV2 pandemic. In the state of Aguascalientes, Mexico, at least 62,400 cases and 3,479 deaths due to COVID-19 have been confirmed so far. As an strategy against SARS-Cov2, many vaccines have been developed, from which only BNT162b2 Pfizer/BioNTech, ChAdOx1 nCov-19/AZD1222 and CoronaVac are available at our state. It has been shown that patients on dialysis and renal trasplantation have a high morbidity and mortality due to COVID-19.
Objective: To assess and compare the seroconversión level (≥100U/ml) in patients with chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis (HD) and kidney transplant recipients (KTR), who received two doses of the BNT162b2 Pfizer/BioNTech, ChAdOx1 nCov-19/AZD1222 and CoronaVac vaccines. To identify the risk factors associated with a suboptimal response of the vaccine received in our study population.
Methods: We conducted a prospective, observational, non-blind, comparative study, which included adult patients from ages 18 to 80 years, both genres, undergoing renal replacement therapy with hemodialysis or kidney trasplantation, who had received two doses from the BNT162b2 Pfizer/BioNTech, ChAdOx1 nCov-19/AZD1222 and CoronaVac vaccines in the last 2-6 months before the sample was taken. Levels of antibodies were determined using the Elecsys anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoassay.
Statistical analysis: Chi-square test with Yates correction, non-paired Student’s T and logistic regression análisis. We considered a p<0.05 value as statistically significant.
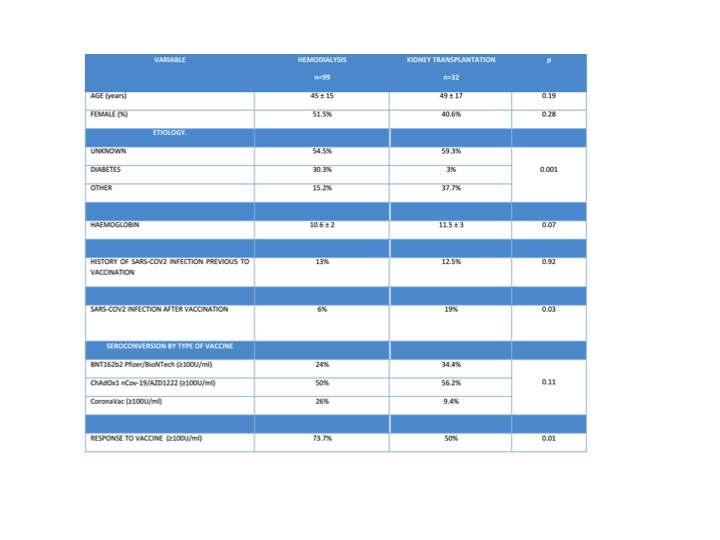
Results: One hundred and thirty-three patients were included, 99 of them were undergoing HD and 32 were KTR. The multiple logistic regression analysis used the seroconversion ≥100 U/mL as a dependent variable, demonstrating that KTR was the risk factor associated to less frequency of seroconversion (p= 0.01, Exp(B) 2.8 with an IC Exp(B) of 1.23-6.40).
Conclusion: Renal replacement therapy with HD was associated with a greater frequency of seroconversión, independently of the type of vaccine received, compared to the kidney transplant receptors. Patients with a kidney transplant exhibited a greater frequency of SARS-COV2 infection after the vaccination, compared to the patients undergoing HD. Kidney transplantation was the main risk fator associated to a smaller rate of conversión, regardless of the type of vaccine.
