Seroconversion in pacients after SARS-cov-2 ChAdOx1 nCoV-19/AZD1222 vaccination in hemodialysis patients and kidney transplant recipients
Alfredo Chew-Wong1, Lizbeth Morales-López1, Elizabeth Hernández-Infante1, José M. Arreola Guerra1, Guadalupe Ricalde-Ríos1, Roberto Roque-Flores1, Luis Romo-Franco1, Mario González-Gámez1, Ana B Lagunas-Rodriguez1, Rafael Reyes-Acevedo1.
1Nephrology and Kidney Transplantation, Centenario Hospital Miguel Hidalgo, Aguascalientes, , Mexico
Background: Since December 2019 the world has been affected for Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. In Aguascalientes state at March 13th 2022 has been confirmed a total of 62,440 cases and 3,479 deaths caused by COVID-19. As a combat strategy were developed different kind of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. The Oxford University developed the vaccine ChAdOx1 nCov-19/AZD1222 which is based in a viral vector which codes the information of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. It has been proven that the morbidity and mortality from COVID-19 is higher in hemodialysis (HD) patients and Kidney Transplant (KT) recipients.
Objective: Measure and compare the seroconversion level in hemodialysis patients and kidney transplant recipients (KTR), who received two doses of the ChAdOx1 nCov-19/AZD1222 vaccine and identify the factors associated with low response to the vaccine used in our study population.
Methods: We performed a prospective, observational, unblinded and comparative analysis. Patients included between 18-80 years old, both genders, that they were in HD or with KTR, and received two doses of the ChAdOx1 nCov-19/AZD1222 vaccine between 2-6 months before sampling. The antibodies level against spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 was determined by the immunoassay Elecsys anti-SARS-CoV-2 and we determined a positive result ≥100 U/mL.
Statistical Analysis: iChi² test with Yates´ correction, Student´s T-Test unpaired and multiple logistic analysis. p<0.05 was considered as significant.
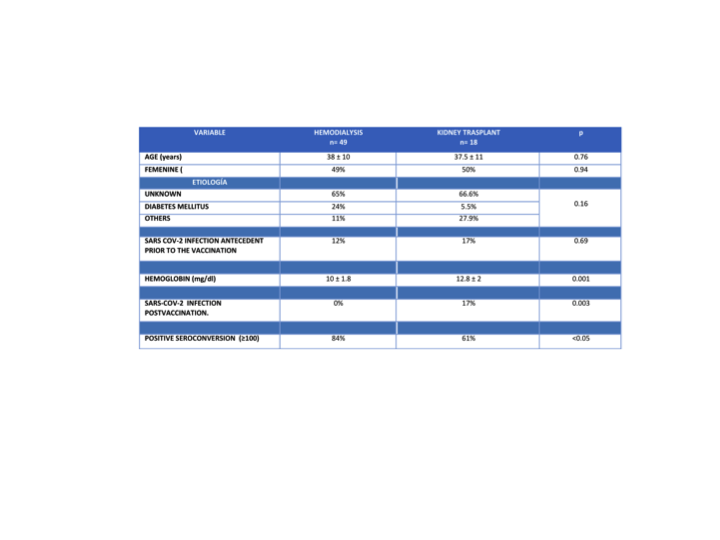
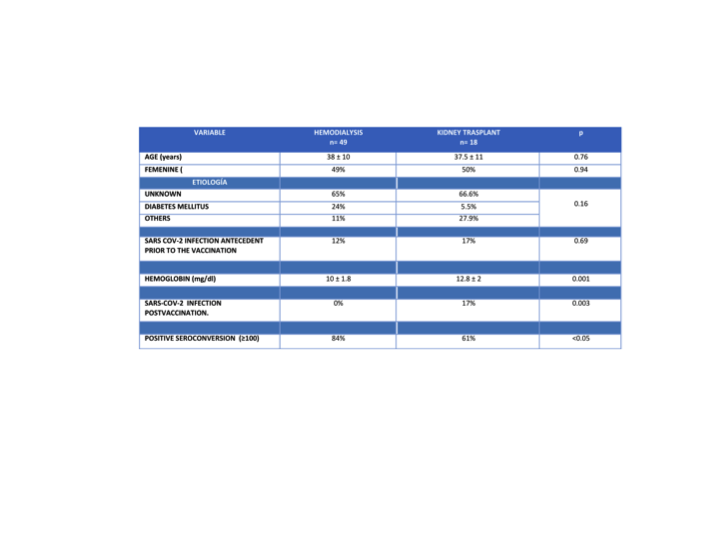
Results: 67 patients were included, 49 in HD and 18 with KTR. In the multiple logistic regression analysis, taking the positive seroconversion ≥100 U/mL as the dependent variable, the KT was the risk factor associated with a lower seroconversion frequency, p<0.05 Exp(B) 3.26.
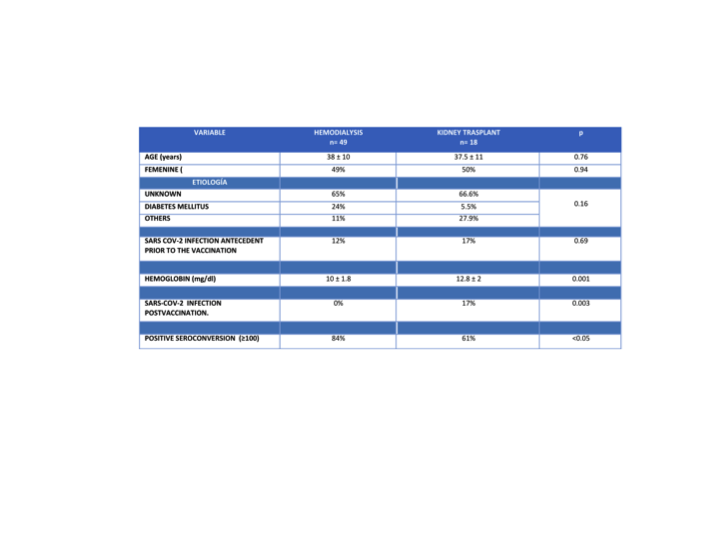
Conclusions: The ChAdOx1 nCov-19/AZD1222 vaccine was associated with a higher seroconversion level in HD patients in comparison to KTR. The KTR patients presented a higher frequency of SARS-COV2 infection post vaccination in relation to HD patients. The main risk factor associated with lower seroconversion response was KT in patients who received the ChAdOx1 nCov-19/AZD1222 vaccine. Our population presented a higher seroconversion response that reported in the literature, probably because of the SARS-COV2 infection antecedent prior to vaccination.
