
Prediction model with quantiferon-CMV for clinically significant cytomegalovirus event in seropositive kidney transplant recipients
Jose Otto Reusing Junior1, Fabiana Agena1, Gustavo A Campana2, Ligia C Pierrotti2,3, Elias David-Neto1.
1Kidney Transplant Service, Hospital das Clínicas, University of São Paulo Medica School, São Paulo, Brazil; 2DASA - Diagnósticos da América, São Paulo, Brazil; 3Infectious Diseases Division, Hospital das Clínicas, University of São Paulo Medica School, São Paulo, Brazil
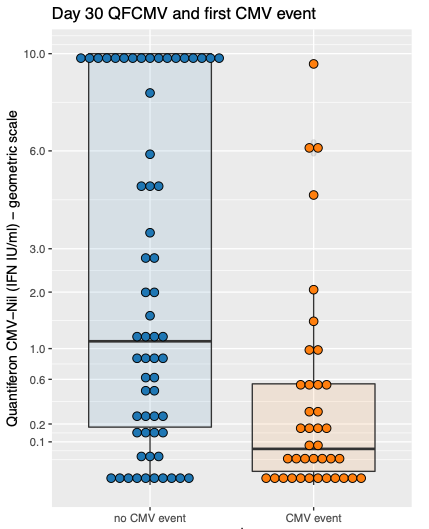
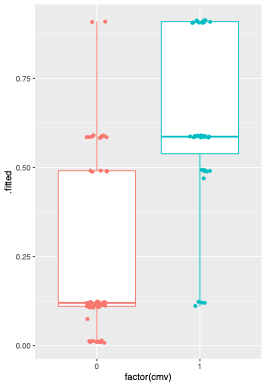
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) disease prevention after kidney transplant (KT) is costly, myelotoxic (universal prophylaxis) and requires a complex logistic routine (preemptive therapy). Quantiferon-CMV (QFCMV) is a simple and commercially available test to assess CMV-specific cellular immunity but has not been widely adopted in clinical practice for risk stratification. In this prospective cohort study, we tested the association of QFCMV and clinical variables with the occurrence of a first clinically significant CMV event (CMV disease or asymptomatic viremia above cutoff for preemptive therapy) in the first year after KT. Logistic regressions were employed to build a prediction model. The cohort comprised 100 KT recipients (mean age 51y, 67% male); all patients were adult, CMV IgG positive (R+), received basiliximab as induction therapy and were maintained on prednisone/mycophenolate/tacrolimus. CMV surveillance with qPCR and pp65 antigenemia was employed weekly until day 98 and then bi-weekly until day 180. Results: 39 patients developed a CMV event (disease 10, asymptomatic infection 29) at median 54 days post-Tx. Day 30 non-reactive/indet. QFCMV (but not pre-Tx) was associated with the outcome, along with deceased donor, higher donor and recipient age, day 30 CD8+ count and cold ischemic time. A higher QFCMV cutoff for reactivity (>0.6 IU IFN-g/ml) outperformed the original cutoff (>0.2) for CMV protection. The final multiple prediction model incorporated 3 variables: day 30 QFCMV (≤ 0.6 IU/ml), deceased donor and recipient age (>60y). After correction for optimism by bootstrap, performance measures were R2 47%, c-statistic 0.85, and corrected calibration slope 0.84. When at least 2 of the 3 variables were present, the model predicted the outcome with sensitivity 90%, specificity 72%, negative predictive value 92%; 48% patients were under this probability threshold. In intermediate-risk kidney recipients (R+, non-ATG), a simple clinical prediction model including day 30 QFCMV identified patients who could be spared from CMV prevention measures. The model requires external validation.
Merck Sharp Dohme Farmacêutica Ltda. Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited. DASA - Diagnósticos da América. Qiagen.
