
She is a Pulmonary Disease Specialist who established the Lung transplant program in 2000 in Iran. In 2004 she also established organ donation program in one of the main Universities of Tehran to increase the rate of organ donation for patients on transplant waiting lists especially on the list of lung transplant which was her main concern. With her colleagues and their hard works they could perform some projects for increasing the donation rate in this University and could get the family consent rate of 96% and make a PMP of 32.4 in its area with 10 million population. She was assigned the Director of Organ donation and Transplantation Office of the Ministry of Health of Iran in 2014. Again her colleagues and she presented some projects to the Minister of Health and with his approval and Iranian Supreme Transplant Council confirmation they started these projects in the country and could increase the organ donation rate in Iran significantly. She also with the best of Iranian Transplant and also Culture and Art experts of Iran established a NGO named "Iranian Society of Organ Donation" to help the Ministry of Health Transplant Management Center especially in issues like Social awareness activities, Donor family support, Donor teams education, research and every other related activities which is needed to improve organ donation and transplantation in Iran. In 2018 responsibility of establishing “Organ donation and Transplantation Registry of Iran” (OTRI), “Organ Transfer System of Iran” (OTSI), Quality assurance and audit of organ procurement units and some other important projects of the Ministry of Health has been passed to ISOD and she with her colleagues in their NGO are hardly working on these important issues. She has been a member of ISODP council and a member of Transplant committee of WHO since 2017 and 2018.She is a Pulmonary Disease Specialist who established the Lung transplant program in 2000 in Iran. In 2004 she also established organ donation program in one of the main Universities of Tehran to increase the rate of organ donation for patients on transplant waiting lists especially on the list of lung transplant which was her main concern. With her colleagues and their hard works they could perform some projects for increasing the donation rate in this University and could get the family consent rate of 96% and make a PMP of 32.4 in its area with 10 million population. She was assigned the Director of Organ donation and Transplantation Office of the Ministry of Health of Iran in 2014. Again her colleagues and she presented some projects to the Minister of Health and with his approval and Iranian Supreme Transplant Council confirmation they started these projects in the country and could increase the organ donation rate in Iran significantly. She also with the best of Iranian Transplant and also Culture and Art experts of Iran established a NGO named "Iranian Society of Organ Donation" to help the Ministry of Health Transplant Management Center especially in issues like Social awareness activities, Donor family support, Donor teams education, research and every other related activities which is needed to improve organ donation and transplantation in Iran. In 2018 responsibility of establishing “Organ donation and Transplantation Registry of Iran” (OTRI), “Organ Transfer System of Iran” (OTSI), Quality assurance and audit of organ procurement units and some other important projects of the Ministry of Health has been passed to ISOD and she with her colleagues in their NGO are hardly working on these important issues. She has been a member of ISODP council and a member of Transplant committee of WHO since 2017 and 2018.
A new successful training method for brain death family approach
Omid Ghobadi1, Katayoun Najafizadeh1, Jamal Rahmani1, Ali Nobakht Haghighi1, Ehsan Radi1.
1Research, Iranian Research Center of Organ Donation, Tehran, Iran (Islamic Republic of)
Introduction: The capability of organ donation coordinators (ODCs) is very critical in getting the family’s consent for organ donation. So, improving this skill in them is a very important matter. One way to improve the success of ODCs in brain death family consent is holding training courses for them. Iranian Family Approach Specific Course (IrFASC) is a novel and unique training method for ODCs. The aim of IrFASC is improving the knowledge level, increasing confidence, and preparing ODC’s for in approaching the brain death families. This study’s aim is to investigate the effects of IrFASC on ODC’s ability and their success in the family consent process.
Methods: Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, a new virtual training course, IrFASC, was designed . This 60-hour training course (5 days long) contained 22 topics on methods of brain death family’s approach. In this course, different sections were designed to increase the impact of the training, consisting of: project-based learning, thinking-based learning, discussion-based learning, brain-storm learning, problem solving, and simulation. IrFASC was held for 3 groups. The first group training course was performed 12 months ago, the second group six months ago and another one three months ago. The success rate of participants in the same intervals (12 months for group 1, six months for group 2, and 3 months for group3) was measured before and after the training course. The success rate of coordinators before and after the training course was compared using the dependent sample t-test.
Results: Thirty volunteers participated in three separate groups in training courses. From them, 11 participants were male. The median confrontation with the family of patient with brain death was 5.5 times (min:2 and max:35) before the training course and 8 times (min:2 and max:40) after the training course. Overall, the training course improved the rate of coordinators’ success (increasing the rate of success from 53.04 to 65.26%, p value=0.003) (table 1). Sub-analysis on groups showed that this improvement is more significant in long periods and the percent of success increased 19.39% in group 1, 8.03% in group 2, and 15.20% in group 3. Furthermore, sub-analysis on coordinators’ gender showed that female coordinators’ improvement was significant during training course (p value =0.02) but this increase was not significant in males (P value=0.06, Table2).
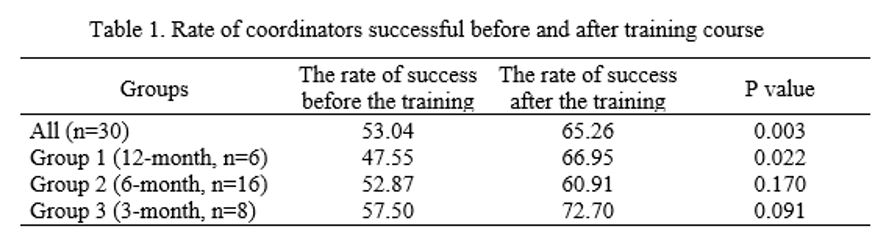
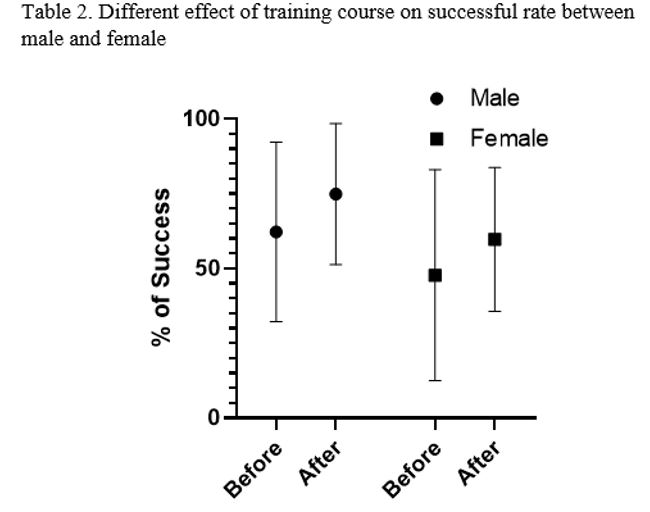
Conclusion: Considering the impact of IrFASC course on improving ODCs’ performance, holding this course for other coordinators is also recommended.

right-click to download
