Retrograde reperfusion of the renal graft in adult recipient to reduce ischemia-reperfusion injury
Myltykbay Rysmakhanov1,2, Gany Kuttymuratov2, Nadiar Mussin1.
1Surgery No2, West Kazakhstan Medical University, Aktobe, Kazakhstan; 2Surgery and Transplantation, Aktobe Medical Center, Aktobe, Kazakhstan
Introduction: Ischemic reperfusion injury (IRI) of a kidney graft is still a current problem in transplantology. The aim of research was study of the effect of retrograde venous renal transplant reperfusion (RVR) on the reduction of IRI in kidney transplant.
Materials and methods: There are seven kidney transplantations in adults from a living donor performed using RVR. Retrospectively analyzed eight recipients’ medical records with typical arterial reperfusion (without RVR). After the standard laparoscopic donors’ nephrectomy, the renal graft washed with a solution of "HTK" with heparin. After applying an end-to-side venous anastomosis, arterial anastomosis applied. At the same time, RVR with venous blood performed. About 80-100 ml of retrograde venous blood flowed from the opening renal transplant artery. Then a typical antegrade reperfusion followed. Immunosuppression was a three-component: CNI + MMF + Steroid with Basiliximab induction in both group. Blood perfusate from the kidney artery collected for blood gas analysis; 1st day diuresis, creatinine and urea analyzed on the 4th and 30th days after surgery and compared with control group. This study registered on clinicaltrail.gov (ID: NCT05179434).
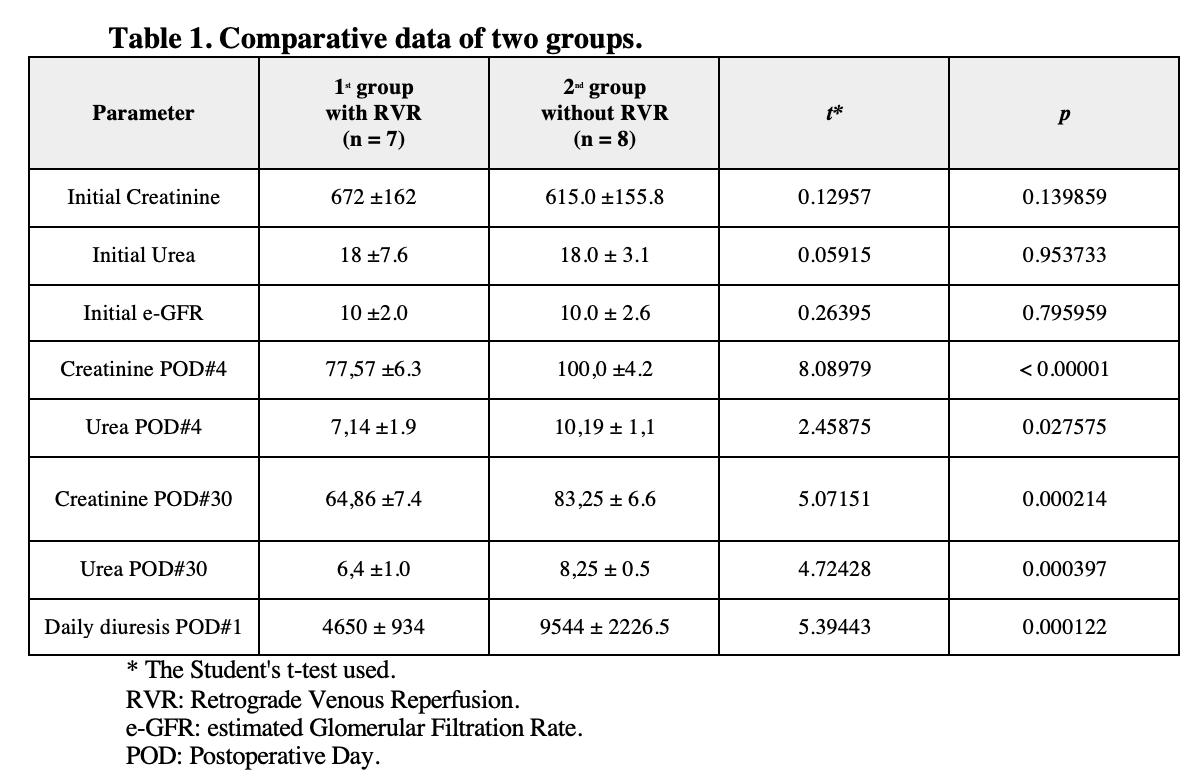
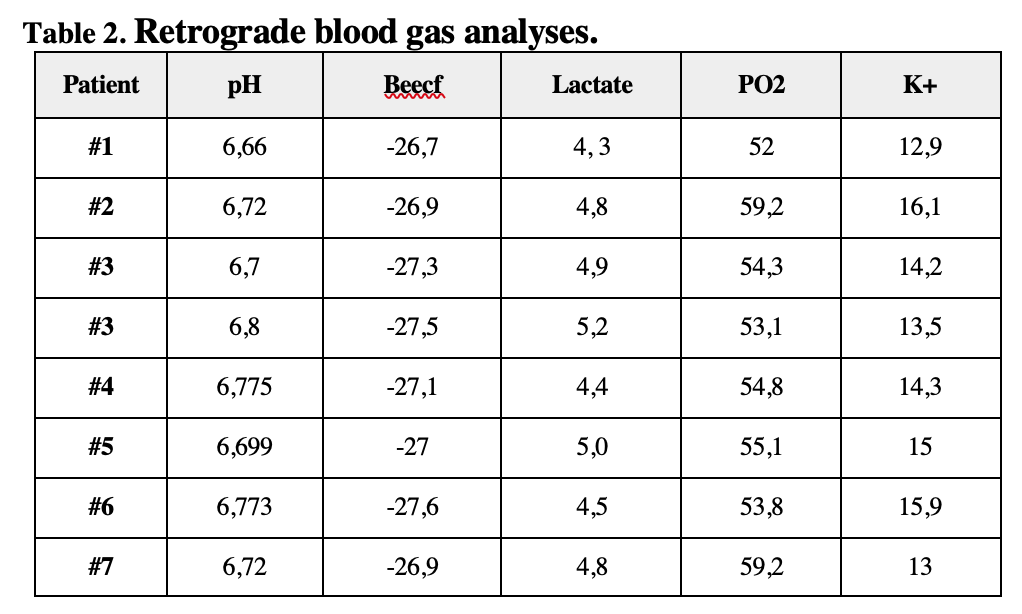
Result: In all cases, the graft function was satisfactory. There were no vascular complications. Significant changes in pH, PO2, BEecf, HCO3−, Lac, K+, and Ca2+values observed in retrograde blood. In the RVR-group daily diuresis in first POD, there was no polyuria, while in the control group there was significant polyuria. Normalization of serum creatinine and urea levels observed on average on the 4th day after surgery (Table 1 and 2).
Conclusion: The results of the initial experience of kidney transplantation using RVR show an improvement in the function of the kidney transplant. In the future, an increase in the cohort of patients is required to study the effect of RVR.

right-click to download
