
A successful program to durability of training effectiveness for organ donation teams
Katayoun Najafizadeh1, Omid Ghobadi1, Ehsan Radi1, Seyed Mohammad Mahdavi1, Jamal Rahmani1.
1Research, Iranian Research Center of Organ Donation, Tehran, Iran (Islamic Republic of)
Introduction: The effectiveness of organ donation team training in improving organ donation status has been proven in various studies around the world. Today, various training courses are held for organ donation teams in the world. However, according to studies, the impact of training courses decreases with the passage of time. Since 2015, a comprehensive training course called IrOSS (Iran OPU Support System) has been held to train organ donation centers in Iran. The program IrOQS (Iranian OPUs Quality control system) was established to evaluate the durability of the impact of training courses and improve the weaknesses of the centers. In the current study, the impact of IrOQS program after the IrOSS course on PMP of the organ donation centers in Iran was evaluated.
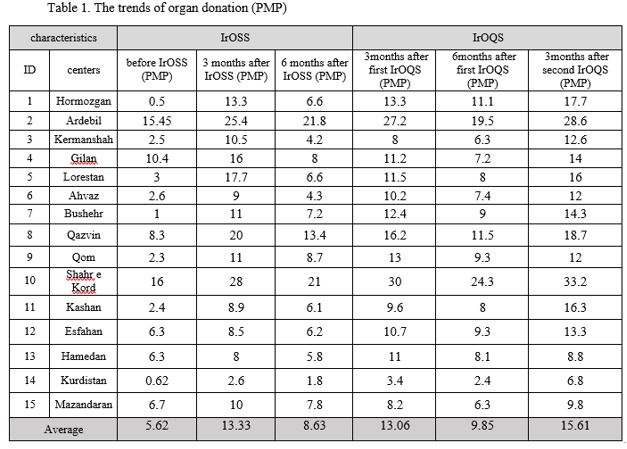
Methods: Totally, 15 donation centers which among 56 country’s centers had a low donation rate were selected and went through IrOSS course. After the training, the IrOQS program was performed seasonally in each center. At each stage of this program, family’s consent rate, donor maintenance, case selection, case detection and brain dead confirmation were evaluated. The weaknesses of the centers were analyzed using the available statistical data. According to the results, solutions were provided and short-term goal-oriented training was also provided. In this study, the PMP of each center before, 3 and 6 months after the IrOSS course and 3 and 6 months after the first stage of IrOQS program and also 3 months after the second stage was calculated and the impact was analyzed.
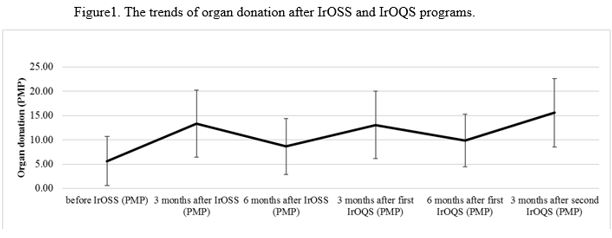
Results: By going through IrOSS courses, the average PMP of regions increased from 5.62 to 13.33 (Table 1) but after 6 months, it declined to 8.63. At this stage, through the IrOQS program, conditions improved and the average PMP increased to 13.06. 6 months after the evaluation program’s first stage, numbers started to decline to 9.85 again which then increased significantly to 15.61 by applying the second stage of the program. The results show that the PMP of the target centers increased significantly (P <0.0001) with the implementation of IrOSS and IrOQS programs (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Based on the results, we can say that training the teams from different regions has a significant but temporary impact on organ donation’s improvement whereas by adding consistent evaluation and support, the impact of training becomes consistent and continual.
