Evidence for xenogeneic hematopoiesis after peripheral blood stem cell transplantation from a novel transgenic pig with knock-in hIL-3 receptor
Erin M Duggan1, Hiroshi Sakai1, Benjamin Piegari1, Sarah Merl1, Nathaly P Llore1, Jeffrey Stern1, Karina Bruestle1, Dominik Hajosi2, Dilrukshi K Ekanayake-Alper1, David H Sachs1, Megan Sykes1, Robert J Hawley1, Adam D Griesemer1.
1Columbia Center for Translational Immunology, Columbia University, New York, NY, United States; 2Institute of Comparative Medicine, Columbia University, New York, NY, United States
Introduction: Xenotransplantation poses a heightened immunologic barrier; therefore, tolerance induction strategies are needed. Mixed chimerism (MC) has successfully induced tolerance in xenogeneic humanized mouse models. In these models, porcine hematopoietic cytokines are needed to support porcine MC. Our study uses a transgenic pig with a humanized IL-3 receptor (Tg hIL-3R) in addition to hCD47 to support engraftment of mobilized porcine peripheral blood stem cells (PBSC) to promote MC in a pig-to-baboon model.
Methods: A novel GalTKO/hCD46/hCD47/hCD55/hCD59 Tg, hCD123/hCD131/hCD116 knock-in pig underwent mobilization with porcine stem cell factor (p-SCF) and porcine IL-3 prior to leukapheresis. PBSC product, dosed at 1x10^9 mononucleated cells/kg, was infused into two P. hamadryas baboons on days 0, 49 and 63 after non-myeloablative conditioning with total body and thymic irradiation, rituximab, ATGAM, LoCD2b and anti-CD154. Tacrolimus and pSCF was given from day 0 to 28. Two control baboons received the same protocol, without PBSC. Donor skin from the donor pig was grafted at week 12 to test tolerance. Controls will be grafted this month. Grafts were serially monitored using punch biopsy and photography.
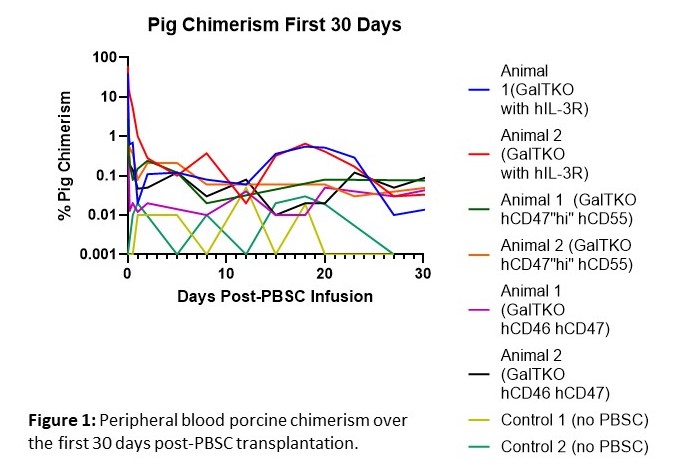
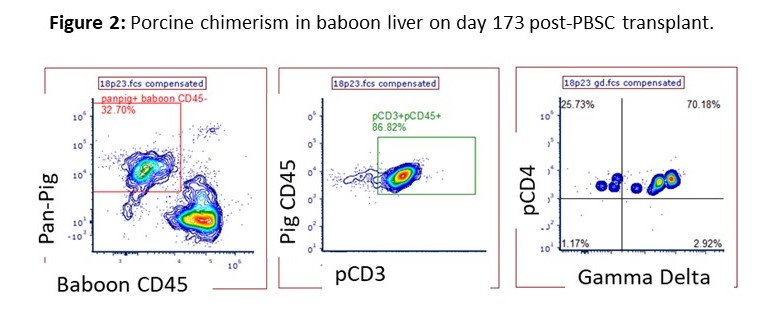
Results: Mobilized porcine PBSC expressed the hGM-CSF and hIL-3R alpha chains, but only the hIL-3R was functional in vitro. Peripheral blood chimerism (PC) was elevated in the first 48-hours compared to current and historical controls that received PBSC from pigs not Tg for hIL-3R. The experimental animals demonstrated a relative increase in PC at day 15-23 compared to all controls. Xeno-antibody levels were reduced from pre-transplant levels until skin grafts rejected, while control animals maintained stable levels during the initial 30 days. Donor skin grafts survived 37 and 41 days, similar to historical MC controls receiving PBSC and skin from GalTKO hCD47hi pigs. After grafts were rejected, the two animals were euthanized and the bone marrow (BM), thymus, liver and lymph nodes were examined for potential engraftment. Porcine lymphocytes were found only in the liver and represented >20% of total live leukocytes for both baboons. These cells were further characterized to be CD3+CD4lo gamma delta T cells.
Conclusion: Due to the remarkable percentage of porcine gamma delta T cells found in the liver at 173 post-infusion, we hypothesize that the liver is an immunoprivileged site for xenogeneic T cells, allowing for cell survival. We continue to explore the infusion of xenogeneic stem cells into protected compartments, such as intra-bone BM transplant, to support porcine stem cell survival. The increase in PC at days 15-23 demonstrates evidence for later stage hematopoiesis in these animals, which has not previously been seen in our studies. This can be attributed to the functional Tg hIL-3R, supporting the hypothesis that genetic engineering of cytokine receptors provides a strategy to enable prolonged MC to promote xenogeneic tolerance.
NIH Award Project Number: 2P01AI045897-21A1- "A Tolerance Approach to Xenotransplantation". ChoironeX.
