Lung procurement: inclusion of modern variables to assess its quality. Descriptive study in a public hospital of the Argentine Republic
Daniel Rodriguez1, Pablo E Centeno1, Federico Puzzo1, Lisandro Sanabria1, Belen Murguía1, Mauricio Petre1, Mariano Domanico1, Ender Duarte1.
1Hospital de Alta Complejidad del Bicentenario de Esteban Echeverría, Buenos Aires, Argentina
Introduction: Over time, the selection criteria for lungs suitable for procurement have been modified. Marginal criteria have even been determined in order to increase the number of potential lung donors. Despite flexibility in the selection criteria, there have been no significant differences in the long-term mortality of patients implanted. In spite of modifications, the PaO2/FiO2 Iindex together with a chest X-ray continue to be the only tools for assessing the state of the lung. The objective of this study is to describe modern variables that might allow identifying the state of the lung in a group of potential lung donor patients in a Public Hospital of the Argentine Republic.
Materials and Methods: Descriptive design study. Data was obtained from the electronic medical record. Patients with a diagnosis of brain death who met the criteria for potential lung donors according to the criteria of the Spanish Transplant Society were included. They had been admitted in our institution between January 1 and December 31, 2021. The following variables were analysed: PaO2/FiO2 Index, Respiratory System Compliance (Csr), Ventilatory Ratio (Rv) and Index y/y. A descriptive statistical analysis was carried out.
Results: 15 patients were included, of which 9 (60%) met ideal criteria and 6 (40%) marginal criteria as lung donors. Table 1 shows the clinical-demographic characteristics. 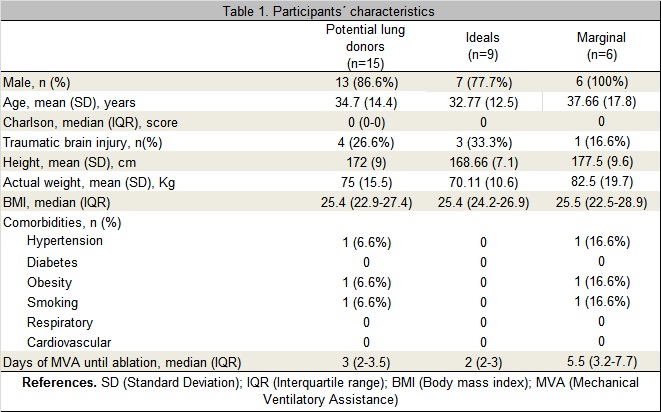
Of the six who met marginal criteria, four were due to time greater than 72 hours of MV, one for PaO2/FiO2 <300 and another one for being a smoker <20 p/year. Table 2 describes the outcome variables and the ventilator setting of the included patients.
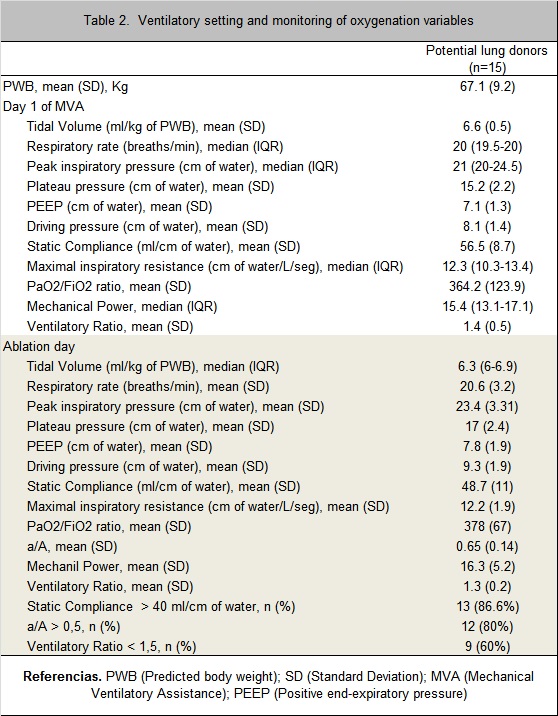
Conclusions: Results show that despite having a good PaO2/FiO2 relationship, there is great variability in the other variables. This leads to the following questions: Can the PaO2/FiO2 variable independently define the quality of a lung? Should new variables be incorporated when choosing a potential lung donor?
Agradecimiento al Dr. Adrian Tarditti por su labor en el desarrollo de nuestra institución y haciendo posible la realización de dichos trabajos de investigación.
