Analysis of ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation in post-COVID-19 candidates: a multicentre, retrospective cohort study from India
Ruchir Dave1, Vivek Kute1, Hari Shankar Meshram1.
1Nephrology and Transplantation, IKDRC-ITS, Ahmedabad, India
Introduction: There is a dearth of data regarding the consequences of ABO-incompatible kidney transplant (ABOiKTx) amongst post-COVID-19 candidates.
Methods: The study was designed as a retrospective, multi-centric cohort study across 11 sites in India, from August 2020 to December 2021. The data for ABOiKTx conducted for post-COVID-19 candidates were investigated. The primary outcome of biopsy-proven acute rejection (BPAR) was compared with the ABO protocol implemented through Kaplan Meier (KM) analysis. The secondary outcomes were graft loss, patient survival, and infections.
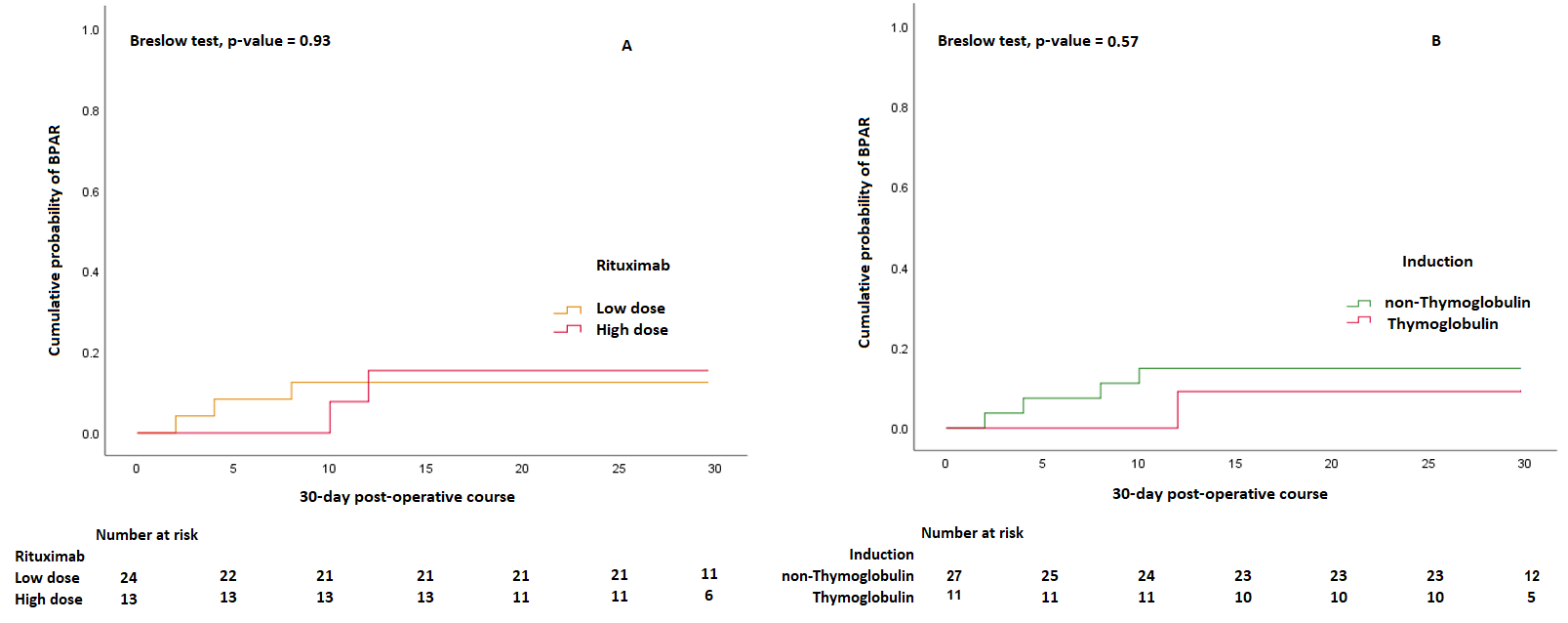
Results: A total of 38 ABOiKTx with candidates of median (Interquartile range) age as 38.5(31.25-47.5) years were performed. 19 cases had a mild illness of COVID-19 severity, while nine (23.6%) had oxygen requirement. Six (15.7%) donors also were post-COVID-19. The most common ABO incompatibility reported was A to O in 14(36.8%) pairs followed by B to O in 10(26.3%) pairs. The maximum isoagglutinin titer cut-off was 1:2048 and 1:64 for baseline and pre-transplant levels respectively. The median time from COVID-19 infection to surgery was 130(63.2-183) days. BPAR, graft loss, and mortality were 13.1%, 2.6%, and 2.6% respectively. The Breslow-Wilcoxon’s p-value in KM plots were 0.57 and 0.93 for thymoglobulin-based induction and high dose rituximab-based regimen respectively. The incidence of re-infection was 2.6%. Two (5.2%) urinary tract infections were reported. No cytomegalovirus or BK Polyomavirus infection was reported. The median serum creatinine at 1-year of follow-up was 1.1(0.8-1.3) mg/dl.
Conclusion: Our report, implies that ABOiKTx in post-COVID-19 candidates can be successfully performed with no major deviation from standard ABO protocol.

right-click to download
