Association of human leukocyte antigen with anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike protein humoral response
Brijesh Yadav1, Narayan Prasad1, Deependra Yadav1, Sonam Gautam1, Ankita Singh1, Ravishankar Kushwaha1, Manas Ranjan Patel1.
1Nephrology and Renal Transplantation, Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow , Lucknow, India
Narayan Prasad.
Introduction: Cellular and humoral response are required for the SARS-CoV-2 eradication. Antigen presenting cells load SARS-CoV-2 peptides on human leukocyte antigen with different avidity and present to T and B cells for the differential humoral and cellular response. Due to immunosuppression, renal transplant recipient patients are speculated to poorly form the antibody against SARS-CoV-2 virus. Therefore, determining the association of specific HLA alleles with anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike protein antibody formation will be helpful in managing the renal transplant recipient patients having specific HLA alleles from SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination.
Material and Methods: In this study anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike protein antibody in 161 renal allograft recipient patients were determined by the chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay methods and human leukocyte antigen alleles were determined by the polymerase chain reaction-single strand oligonucleotide methods and analyzed to study, the HLA alleles association with anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike protein humoral response and severity of COVID-19 symptoms in recently SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. Seroconversion was defined if anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike protein antibody titer was >50AU/ml.
Results: The anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike protein antibody seroconversion rate in renal allograft recipients was 90.06% with median titer 751.80 AU/ml. The frequency of HLA class I alleles A*11 was in 22.1%, A*24 in 21.37%, A*33 in 20.68%, HLA B*15 in 11%, B*07 in 8.27%, HLA-C*30 in 20.93% and C*70 in 23.25% and Class II HLA alleles -DRB1*07 was in 18.62%, DRB1*04 in 13.8%, HLA-DRB1*10 in 14.48% and HLA-DQA1*50 in 32.55% of patient and were associated with the seroconversion.
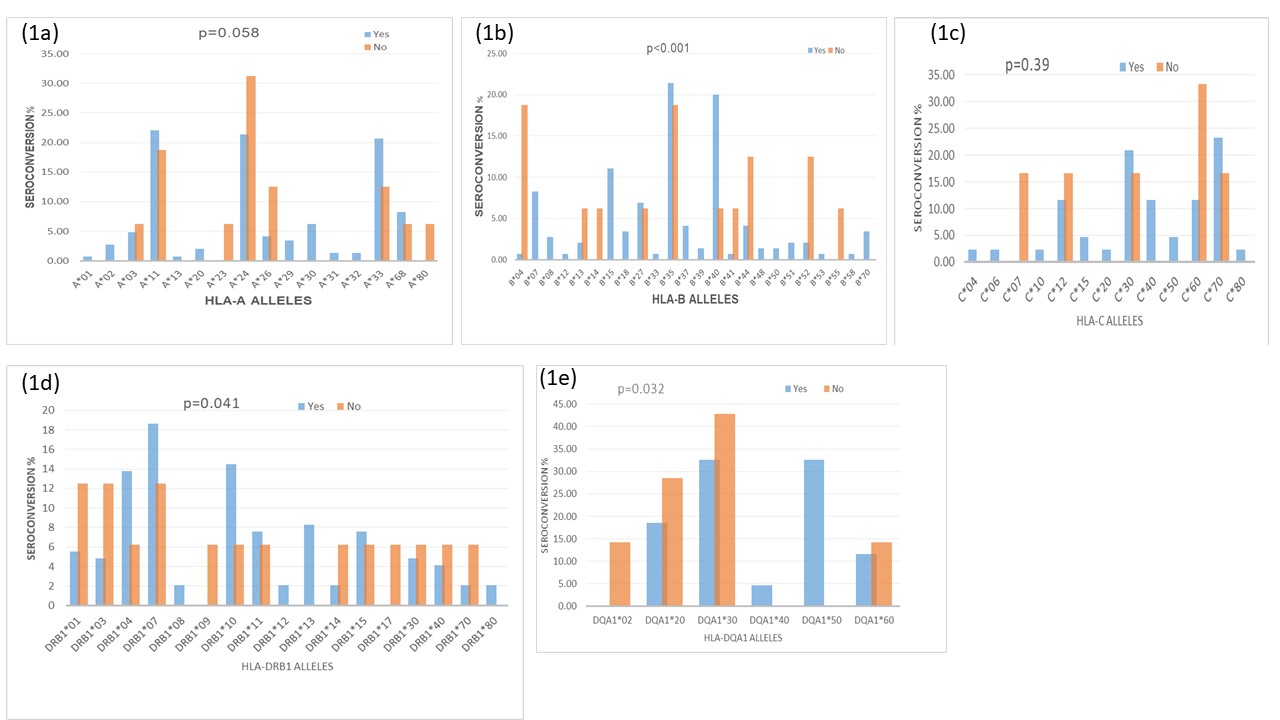
HLA-B*04, B*52, and B*55 were associated with non-seroconversion in 18.75%, 12.5 and 6.25% of patients respectively, HLA- C*07, C*12, C*30 in 16.6% of patients and C*60 in 33.3% of patients were associated with non-seroconversion. HLA-DRB1*01, HLA-DRB1*03 in 12.5% and DRB1*70 in 6.25% of patients were associated with non- seroconversion. The mean post-infection time of patients recovery from COVID19 symptoms was 18.25±8.14 days.
Conclusion: Renal transplant recipients with SARS-CoV-2 infection developed a robust seroconversion rate of 90.0% and different alleles of HLA-B, DRB1 and DQA1 were significantly associated with the seroconversion.

right-click to download
