Tolerance of allogeneic kidneys with durable (>365 days) multilineage chimerism and bone marrow engraftment in cynomolgus macaques
Daniel Eisenson1, Yu Hisadome1, Yuji Tomori1, Michelle Santillan1, Kazuhiro Takeuchi1, Christene Huang1, David Sachs1, Megan Sykes1, Kazuhiko Yamada1.
1Columbia Center for Translational Immunology, Columbia University, New York, NY, United States
Background: We have previously reported that a regimen including anti-CD3 immunotoxin, cyclosporine, and pre-transplant total body irradiation (TBI) promoted tolerance of kidney allografts and enabled complete withdrawal of immunosuppression with transient chimerism in non-human primates. Donor islets were also tolerated when transplanted in composite islet-kidney (IK) grafts. However, data from a rodent model demonstrated that durable chimerism may be required to reverse the autoimmunity responsible for type-1 diabetes (T1D). As the first step toward our goal of curing T1D and diabetic nephropathy by transplantation of IKs, we aimed to develop a clinically applicable protocol to induce tolerance of allogeneic kidneys with >6 months durable chimerism in NHPs.
Methods: Cynomolgus macaques received one-haplotype mismatched, mobilized peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (PBHSCTx) on Day 0 followed by donor kidney Tx (DKTx) on Day 42. Recipients in Group 1 (n=5) received PBHSCTx that contained 3.7-20x10^7 CD34+ cells/kg recipient body weight (bwt). Recipients in Group 2 (n=5) received PBHSCTx containing a lower dose of CD34+ cells (2x10^7 cells/kg bwt). All recipients received Rituximab, rATG, and 100cGy of TBI before PBHSCTx. Tacrolimus was administered daily starting on Day -1 and was stopped at Day 41 after PBHSCTx. Anti-CD40mAb was administered twice weekly until 30 days after DKTx (72 days after PBHSCTx).
Results: All animals developed and maintained multilineage chimerism with evidence of bone marrow (BM) engraftment throughout the experimental period. However, all animals who received PBHSCTx with high numbers of CD34+ cells (Group 1) were euthanized due to GVHD or cytokine storm at early time points (Days 33, 43, 45, 55, 92). In contrast, recipients who underwent PBHSCTx with lower numbers of CD34+ cells at 2x10^7 cells/kg bwt (Group 2) had no evidence of GVHD or cytokine storm and had significantly prolonged survival (p<0.02). Although two animals were euthanized at Day 118 and 218 days due to CMV infection, all animals maintained macrochimerism throughout the experimental period. All three animals who received appropriate CMV therapy had stable clinical courses, and accepted kidneys (two from actual HSCTx donors and one from a donor with Class II DRα matched to the HSC donor) that were transplanted 42 days after PBHSCTx without any episode of rejection crisis (currently >368, >194 and >143 days). Notably, the longest-term follow-up animal (>368 days) maintains multilineage peripheral chimerism as well as clear BM chimerism. Furthermore, in vitro data showed donor-specific unresponsiveness in vitro and donor-derived recent thymic emigrants.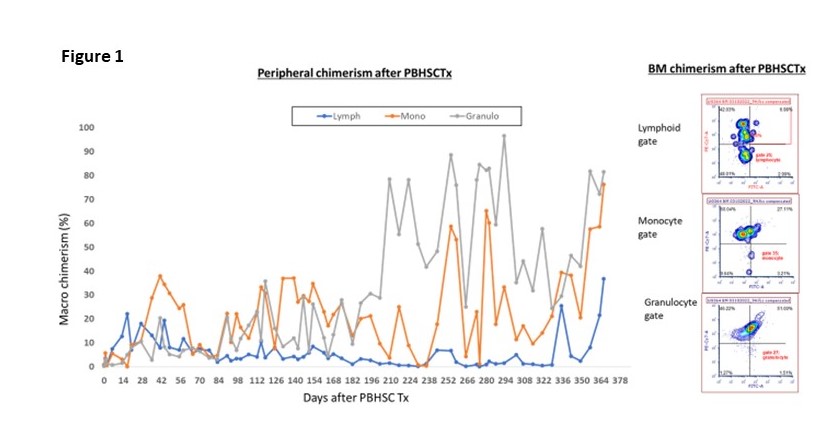
Conclusions: To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of reproducible, >365 days multilineage durable chimerism with BM engraftment and kidney graft tolerance in a cynomolgus HSCTx and kidney Tx model. Achieving long-term durable chimerism, which may be necessary to overcome autoimmunity of T1DM, allows us to confidently extend this protocol to composite IK Tx and move one step closer to a clinical trial.

right-click to download
