Non-invasive assessment of renal allograft fibrosis by shearwave elastography: a radiological – pathological correlation analysis
Dr Sandeep Singhal1, Dr Umapati Hegde2, Dr Mohan Rajapurkar2, Dr Sishir Gang2, Dr Abhijit Konnur2, Dr Hardik Patel2.
1Nephrology Resident, Muljibhai Patel Urological Hospital, Nadiad, Gujarat, India; 2Nephrology Consultant, Muljibhai Patel Urological Hospital, Nadiad, Gujarat, India
Background & objectives: Currently, renal allograft biopsy is the only reliable tool available to detect fibrosis in the transplanted kidney. However, it is an invasive procedure and is associated with complications. Therefore, a non-invasive tool to detect renal allograft fibrosis is needed. This study sought to evaluate the usefulness of SWE in the quantitative measurement of renal allograft fibrosis and to correlate shear-wave sonoelastography measurements with histological findings, resistive index, serum creatinine level and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) obtained with the CKD-EPI.
Methods: A cross-sectional study of 110 renal transplant patients. Patients were classified as having stable allograft and allograft dysfunction based on clinical parameters. Only patients with allograft dysfunction underwent renal allograft biopsy. SWE assessment was done by a single radiologist using the same ultrasound machine to quantify allograft fibrosis in kPa. Renal allograft biopsies were interpreted by the same pathologist according to the 2019 Banff classification. The potential correlation between SWE scores and Banff classification was performed in allograft dysfunction group. The receiver operating characteristic curves were drawn to evaluate the likelihood of differentiation.
Results: 66 patients had allograft dysfunction and 44 patients had stable allograft function. Mean parenchymal stiffness measured values in stable allograft and allograft dysfunction were 14.20±4.50 kPa and 16.54±5.42 kPa respectively.
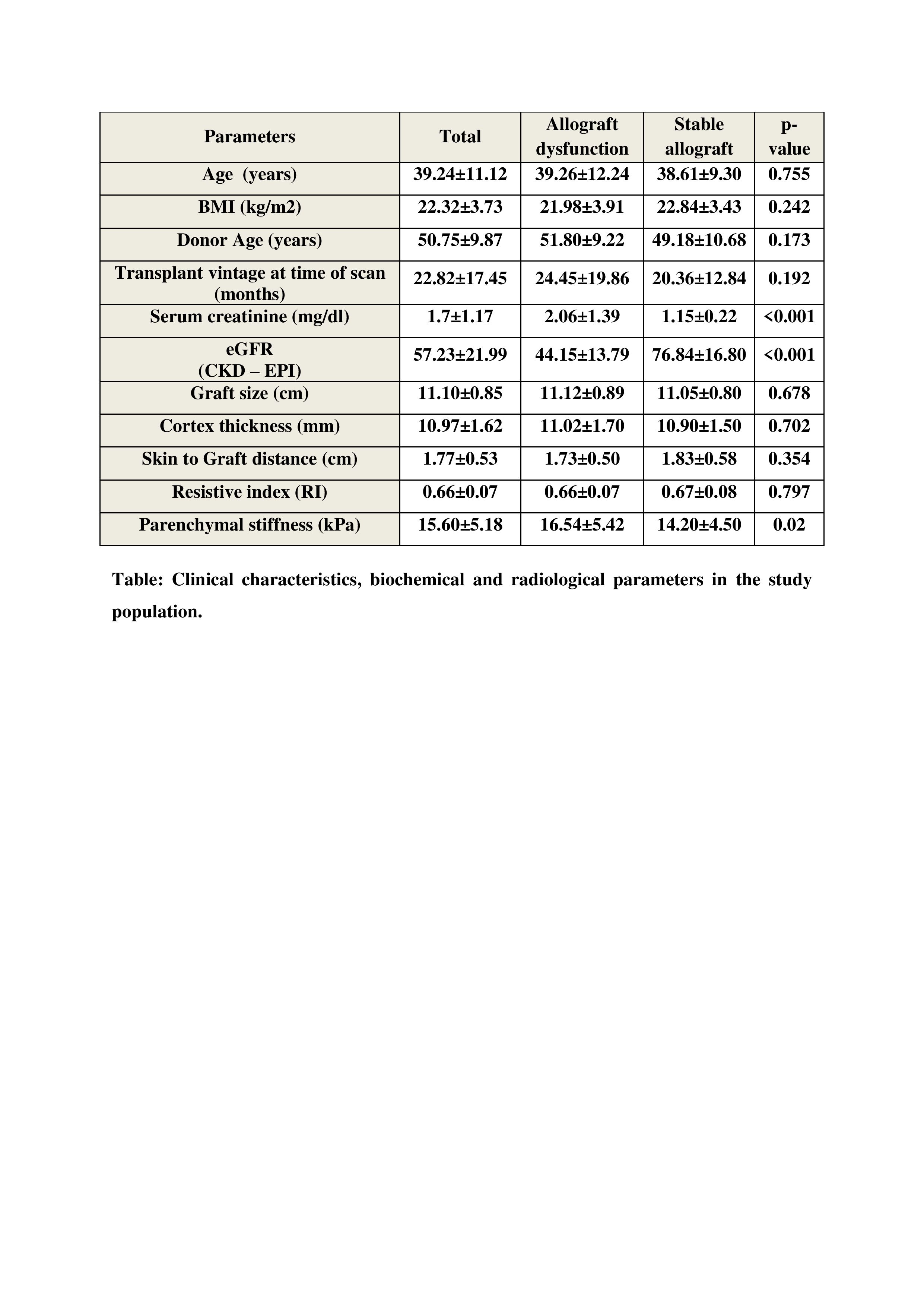
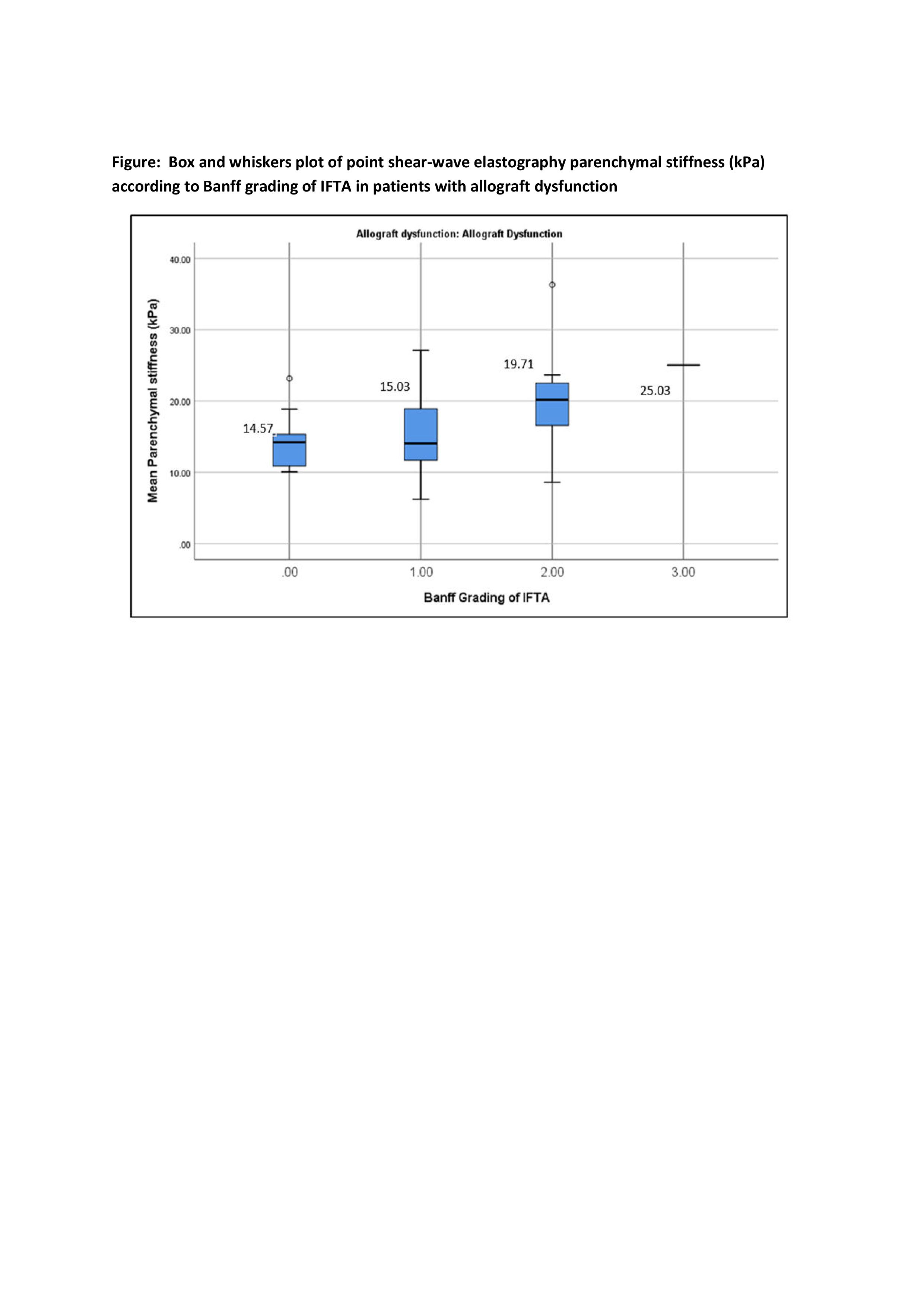
Mean parenchymal stiffness showed a significant negative correlation with eGFR (r= -0.317, p= 0.001) and a positive correlation with serum creatinine level (r= 0.256; p= 0.007). There was a significant correlation between the Banff grade of IFTA and the mean SWE score, (p= 0.003).
The correlation of resistive index was insignificant when compared to the mean SWE score (r= 0.058, p= 0.547). The area under the curve was higher and significant at IFTA grading ≥ 2 (AUC- 0.801, p < 0.0001) when compared it with IFTA grading 0 (AUC–0.523, p= 0.831) and 1 (AUC-0.551, p= 0.431).
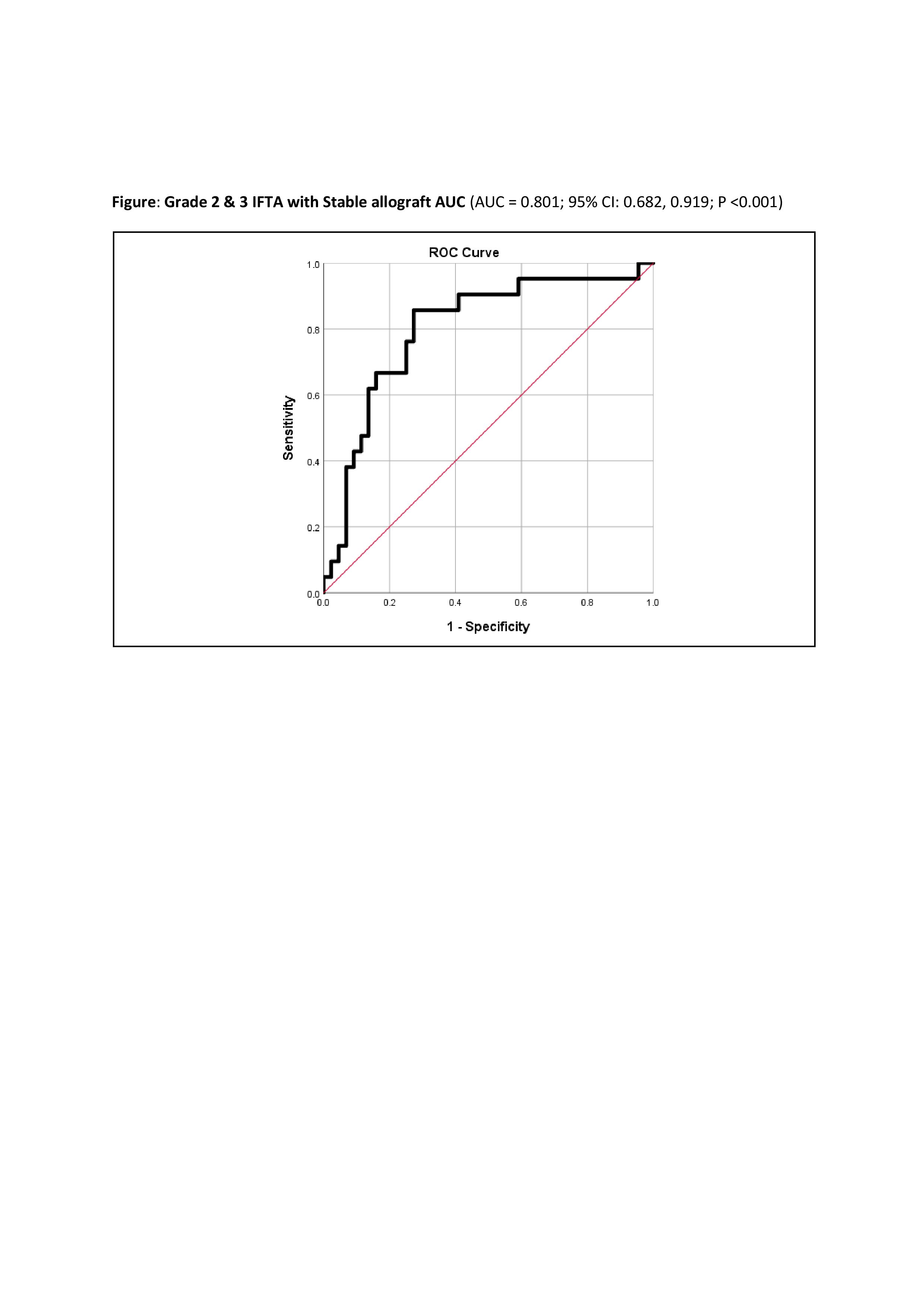
The sensitivity was 86% and specificity was 73% in the differentiation of stable graft from graft dysfunction with moderate to severe fibrosis (cut-off value, 16.15 kPa). The sensitivity was 85% and specificity was 67% in the differentiation of graft dysfunction with grade 2/3 IFTA from graft dysfunction with grade 0/1 IFTA (cut-off value, 16 kPa). This means that shear wave elastography effectively detects moderate to severe fibrosis in the allograft. The severity of fibrosis increased with the increase in transplant vintage with statistical significance (p <0.001).
Conclusions: Renal allograft parenchymal stiffness quantified by shear-wave elastography showed a significant correlation with allograft fibrosis graded by Banff classification. SWE can differentiate between mild fibrosis and moderate‑to‑severe fibrosis with high accuracy. The inverse correlation of parenchymal stiffness with eGFR and positive correlation with serum creatinine level show that shear-wave sonoelastography may reflect the functional status of the renal allograft. Therefore, shear wave elastography can be used as a noninvasive tool to assess renal allograft fibrosis and is better than the resistive index.
Key words: elastography, SWE, renal allograft biopsy, renal transplant, allograft fibrosis.

right-click to download
