Antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in kidney transplant recipients
Ali Mahgoub1, Mohamad Alkadi1,3, Essa Abuhelaiqa1,3, Rasha Abdul Rahman1, Hiba Tohid1, Laith Abu Raddad3, Peter Coyle2, Hassan Al-Malki1,2.
1Nephrology department, Hamad medical corporation, Doha, Qatar; 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Hamad medical corporation, Doha, Qatar; 3Weill Cornell Medical College in Qatar , Doha, Qatar
Introduction: Kidney transplant recipients are vulnerable to developing a severe form of COVID19 infection. Although severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) mRNA vaccine has significantly improved incidence of COVID19, seroconversion rates in immunosuppressed patients post-vaccine are variable and unpredictable. We aimed to evaluate the rates of antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine, identify factors affecting immunogenicity, determine risk of infection and severity of COVID-19 infection among kidney transplant recipients.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 372 kidney transplant recipients who fulfilled the criteria. We categorized patients into three groups; previous infection, seronegative and seropositive patients. SARS-CoV-2 antibody response, risk factors associated with negative serology and patient’s outcomes were evaluated.
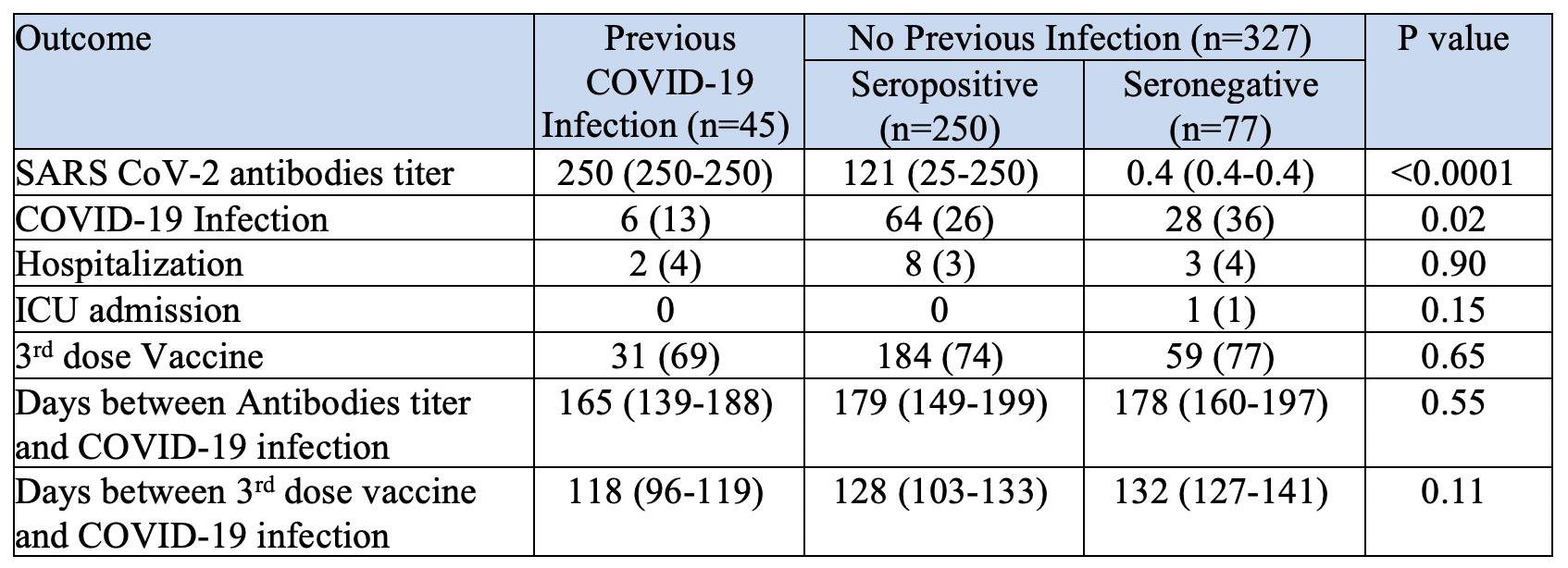
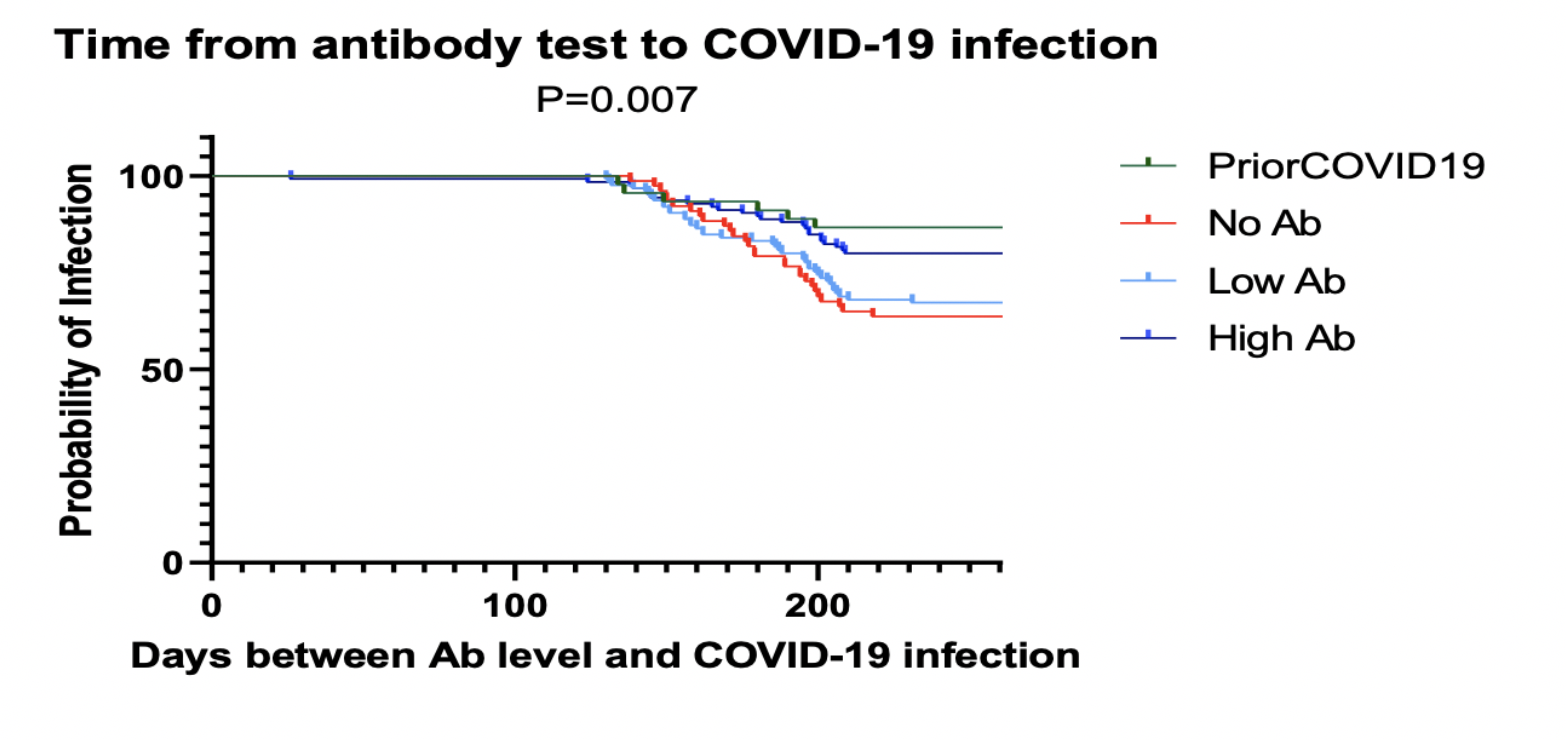
Results: There were 45 patients who had previous COVID-19 infection before measurement of anti SARS-Cov-2 antibodies; 20 patients before vaccination, 6 patients after the first dose of vaccine and 19 patients after the second dose. Of the remaining 327 patients, there were 250 patients (76%) who had seroconversion which were further categorized into low antibody (n=125) and high antibody groups. Factors associated with lower seroconversion included older age (p=0.06) and female gender (p=0.03), however Race, immunosuppression regimen, and trough levels were not significant. Analysis of variables associated with lower antibodies titer revealed older age (p= <0.0001), race (p= 0.02), history of diabetes (p= 0.04), and longer duration between antibodies titer measurement and 2nd dose of vaccine (p= 0.002) were significant. It was also found that seropositivity and previous COVID-19 Infection was associated with lower incidence of COVID-19 infection and Hospitalizations (Table 1, Figure 1).
Conclusion: Understanding the immunologic response to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients is important to prevent life threatening infection. Identification of transplant recipients at risk of low vaccine response can be a guide to formulate personalized therapy.

right-click to download
